Introduction to Breeding Budgerigars for Specific Colors and Patterns
Breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns can be a fascinating and rewarding hobby. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced breeder, understanding the genetics behind these colorful pet birds is essential to achieving your desired results. In this guide, we’ll explore the secrets to breeding beautiful budgerigars, helping you achieve your dream budgie colors through breeding.
Budgerigars, often simply called budgies or parakeets, are known for their vibrant plumage and lively personalities. By selectively breeding pairs, you can enhance and produce a wide variety of stunning colors and patterns. But where do you start?
Understanding Budgerigar Genetics
The first step in breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns is to understand the basics of budgerigar genetics. This involves knowing how different genes interact to produce various color mutations. Breeding pet birds for beginners can be simplified by focusing on a few key genetic principles. For instance, knowing whether a color trait is dominant or recessive will help you predict the outcome of your breeding efforts.
Selecting the Right Breeding Pairs
Once you have a grasp of genetics, the next step is selecting the right breeding pairs. Choosing pairs with complementary genetic backgrounds increases the likelihood of producing the desired color mutations. For example, if you’re interested in breeding blue budgerigars, you’ll want to select pairs that carry the blue color gene.
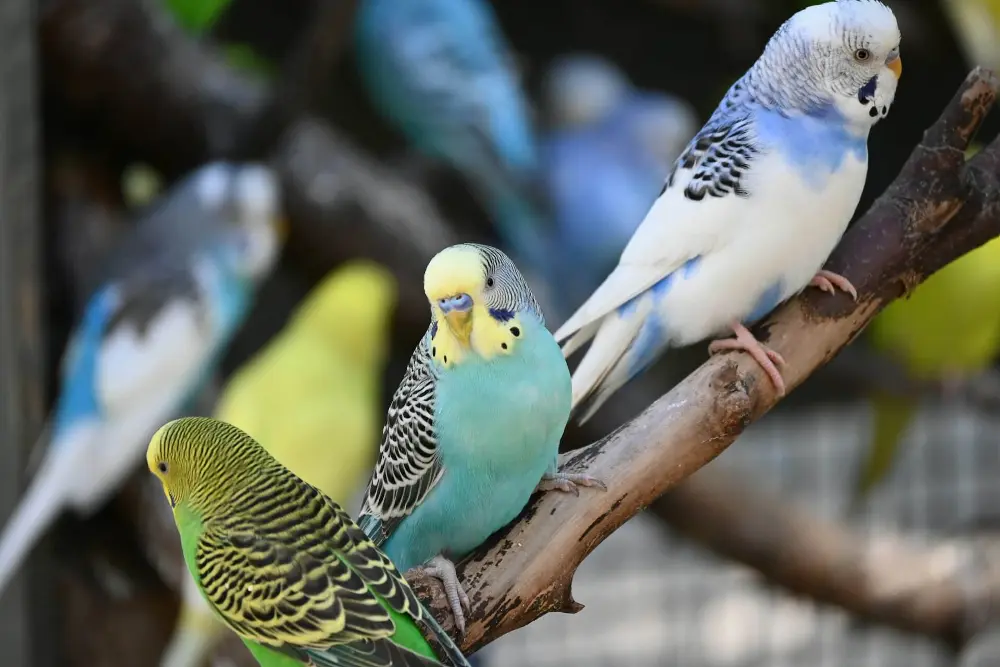

A vibrant mix of budgerigars displaying various color mutations, perched on a branch in an aviary.
Creating the Ideal Breeding Environment
Creating an ideal breeding environment is crucial for the health and success of your budgerigar breeding program. Ensure your breeding cage setup is spacious and well-equipped with all necessary supplies. Proper nutrition and care also play a significant role in the breeding process.
The Joy of Breeding Colorful Budgerigars
Breeding budgerigars is not just about genetics and environment; it’s also about the joy of seeing your efforts come to fruition. Watching baby budgies grow into beautiful, colorful adults is incredibly rewarding. As you gain experience, you’ll become more adept at predicting and achieving specific color patterns, from breeding lutino budgerigars to creating pied and albino varieties.
In conclusion, breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns is a delightful journey that combines science, care, and a bit of art. By understanding genetics, selecting the right pairs, and providing a suitable environment, you can successfully breed budgies with stunning colors and patterns. Whether you’re aiming for rare budgie colors or simply want to enhance your flock, this guide will set you on the path to becoming a successful budgerigar breeder. Stay tuned for more detailed tips and tricks in the following sections of this comprehensive breeding guide.
Understanding Budgerigar Genetics
When it comes to breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns, understanding the underlying genetics is crucial. Genetics determine the variety of color mutations and patterns that make each budgerigar unique. In this section, we’ll break down the basics of budgerigar genetics in a simple and engaging way.
The Basics of Budgerigar Genetics
Budgerigar genetics might sound complicated, but it’s actually quite fascinating once you get the hang of it. Just like humans, budgerigars inherit traits from both their parents. These traits are controlled by genes, which come in pairs. Each gene can be dominant or recessive, and this determines how a particular trait is expressed.
Dominant and Recessive Genes
To breed budgerigars with specific colors, you need to understand the difference between dominant and recessive genes. Dominant genes are the ones that are more likely to be expressed in the bird’s appearance. For instance, if a budgie inherits a dominant color gene from one parent, that color will typically show up in its plumage.
Recessive genes, on the other hand, only show up when a budgie inherits the same recessive gene from both parents. This is why certain rare budgie colors, like albino or lutino, require careful pair selection.
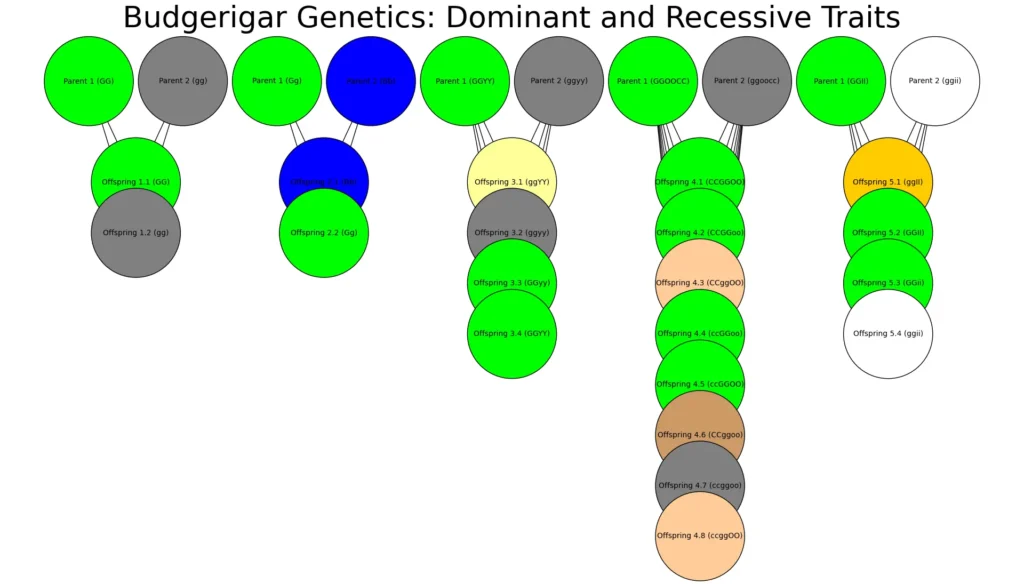
A detailed diagram illustrating the dominant and recessive genetic traits in budgerigars, crucial for breeding specific colors and patterns.
Common Color Mutations
Budgerigars come in a rainbow of colors, thanks to various mutations. Some common color mutations include:
- Blue Budgerigars: Blue is a recessive trait, so to breed blue budgerigars, both parents must carry the blue gene.
- Lutino Budgerigars: Lutino is a mutation that removes all melanin, resulting in a bright yellow bird with red eyes.
- Pied Budgerigars: Pied patterns result from a mutation that causes irregular patches of color and are dominant.
- Albino Budgerigars: Like lutino, albino budgies lack melanin but are white with red eyes.
- Cinnamon Budgerigars: Cinnamon is a sex-linked recessive mutation that lightens the color of the bird’s markings.
Predicting Color Outcomes
To predict the color outcomes of your breeding pairs, you’ll need to know the genetic makeup of the parents. This involves understanding their color genes and whether those genes are dominant or recessive. There are tools and charts available that can help you map out potential color combinations.
Practical Breeding Tips
When breeding for specific colors, start with pairs that carry the genes for the colors you desire. If you want to breed blue budgerigars, both parents need to carry the blue gene. For rarer colors, like albino or lutino, you’ll need to carefully select pairs that both carry the recessive genes.
Understanding budgerigar genetics is key to successfully breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns. By grasping the basics of dominant and recessive genes, and familiarizing yourself with common color mutations, you can predict and achieve the vibrant budgie colors you aim for. In the next sections, we’ll dive deeper into selecting breeding pairs and creating the ideal environment for your budgerigars. Stay tuned for more insights and tips on becoming a successful budgerigar breeder.
Selecting Breeding Pairs
Selecting the right breeding pairs is crucial when it comes to breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns. The success of your breeding program largely depends on the genetic makeup of the pairs you choose. In this section, we’ll discuss how to select breeding pairs that will help you achieve your desired budgerigar color mutations and patterns.
Know Your Budgerigars’ Genetics
Before selecting breeding pairs, it’s essential to understand the genetic background of your budgerigars. Knowing whether your birds carry dominant or recessive genes for certain colors can help you predict the outcome of your breeding efforts. For instance, if you’re aiming to breed blue budgerigars, both parents need to carry the recessive blue gene.
Health and Vitality
Always prioritize the health and vitality of your breeding pairs. Healthy birds are more likely to produce strong, vibrant offspring. Look for budgerigars that are active, have bright eyes, and clean feathers. Avoid breeding birds with any signs of illness or genetic defects, as this can lead to health issues in the chicks.
Age and Maturity
Selecting budgerigars of the right age and maturity is also important. Birds should be at least one year old before they are bred, as this ensures they are physically mature and ready for the demands of breeding. Younger birds may not be fully developed and could face complications during the breeding process.
Compatibility
Budgerigars, like all animals, need to be compatible with their mates. Observe your birds to ensure they get along well and display mutual affection. Birds that are not compatible may fight, which can lead to stress and unsuccessful breeding attempts.

A pair of budgerigars, one yellow and one blue, sharing a cozy corner in their breeding cage.
Specific Color Mutations
If you’re targeting specific color mutations, choose pairs that carry the genes for those colors. Here are a few examples:
- Breeding Blue Budgerigars: Both parents should carry the blue gene.
- Breeding Lutino Budgerigars: Select pairs that have the potential to produce lutino offspring by carrying the necessary recessive genes.
- How to Breed Pied Budgies: One or both parents should carry the dominant pied gene.
- Breeding Albino Budgerigars: Both parents must carry the albino gene to produce albino chicks.
- Breeding Cinnamon Budgerigars: Look for birds that carry the cinnamon mutation.
Record Keeping
Keep detailed records of your breeding pairs, including their genetic backgrounds, health history, and breeding outcomes. This information can help you make informed decisions in future breeding efforts and track the success of different pairings.
Practical Tips
- Introduce pairs gradually: Allow the birds to get to know each other in a neutral space before moving them to the breeding cage.
- Monitor behavior: Watch for signs of aggression or bonding to ensure compatibility.
- Provide a comfortable environment: Ensure the breeding cage is spacious and equipped with all necessary supplies.
Selecting the right breeding pairs is a fundamental step in breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns. By understanding your birds’ genetics, prioritizing health and compatibility, and choosing pairs based on their potential to produce desired mutations, you can set your breeding program up for success. In the next sections, we’ll cover creating the ideal breeding environment and caring for your budgerigars throughout the breeding process. Stay tuned for more valuable insights and tips.
Common Budgerigar Color Mutations
Budgerigars are known for their dazzling array of colors and patterns, making them one of the most popular pet birds. Understanding common budgerigar color mutations is essential for breeders aiming to produce specific colors and patterns. In this section, we will explore some of the most common and sought-after budgerigar color mutations.
Blue Budgerigars
One of the most popular color mutations, blue budgerigars are a striking sight with their vivid blue feathers. This color mutation is recessive, meaning both parents need to carry the blue gene to produce blue offspring. Breeding blue budgerigars can result in shades ranging from light sky blue to deep cobalt.
Lutino Budgerigars
Lutino budgerigars are known for their bright yellow plumage and red eyes. This mutation removes all melanin, leaving only the yellow pigment. To breed lutino budgerigars, you need to pair birds that carry the recessive lutino gene. Lutino budgies are not only beautiful but also quite rare, making them a prized addition to any aviary.
Pied Budgerigars
Pied budgerigars display a mix of colors with irregular patches of their base color and white or yellow. This dominant mutation creates a unique and attractive pattern that is highly sought after. To breed pied budgies, at least one parent must carry the dominant pied gene. The result is a stunning bird with a patchwork of colors.
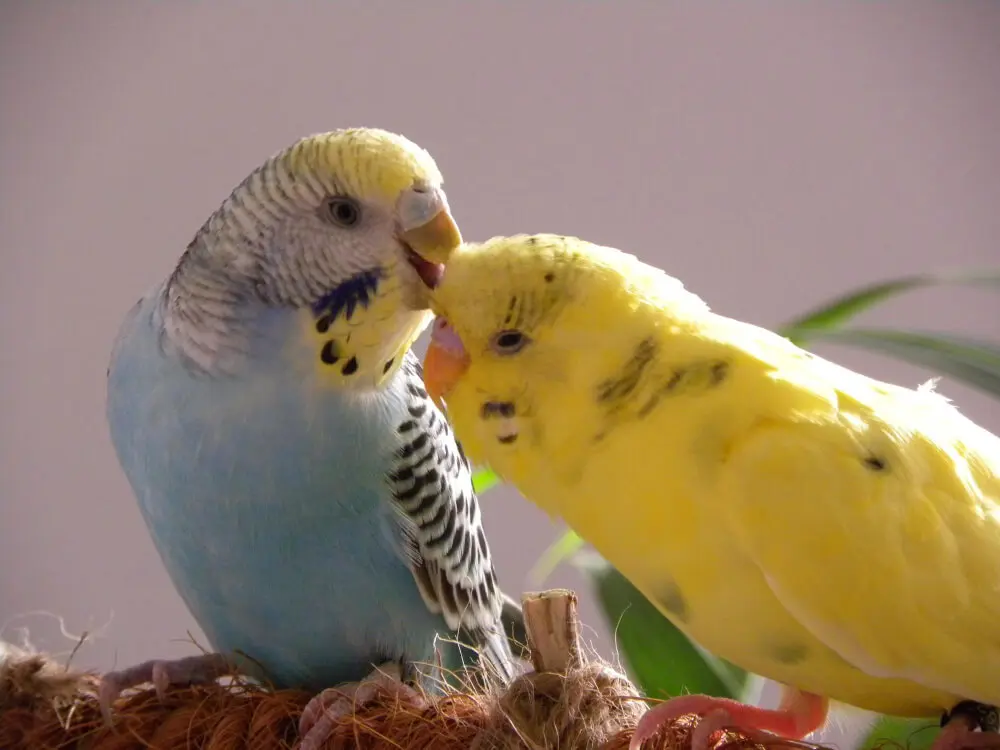

A pair of lutino pied budgerigars, featuring blue and yellow plumage, engaging in affectionate behavior.
Albino Budgerigars
Albino budgerigars are pure white with red eyes, a result of the complete absence of melanin. This recessive mutation requires both parents to carry the albino gene. Albinos are particularly striking and often a favorite among breeders and pet owners alike.
Cinnamon Budgerigars
Cinnamon budgerigars have a warm, brownish hue to their markings instead of the typical black or grey. This sex-linked recessive mutation lightens the bird’s markings, creating a soft, appealing look. Breeding cinnamon budgerigars requires understanding of sex-linked genetics, as this mutation is carried on the sex chromosomes.
Opaline Budgerigars
Opaline budgerigars have a unique pattern that changes the distribution of their markings. This mutation often results in a more vibrant and colorful bird, as it allows the base color to show through more prominently. The opaline gene is a dominant trait, so only one parent needs to carry the gene to produce opaline offspring.
Spangle Budgerigars
Spangle budgerigars have a distinctive pattern where the edges of their feathers are lighter, creating a spangled effect. This mutation is dominant, making it relatively easy to produce spangle offspring. Spangle budgies are eye-catching and a great addition to any breeding program.
Greywing Budgerigars
Greywing budgerigars have diluted markings and a softer overall appearance. This recessive mutation reduces the intensity of the bird’s normal color, giving them a pastel-like look. Breeding greywing budgerigars requires both parents to carry the greywing gene.
Understanding and recognizing common budgerigar color mutations is crucial for any breeder looking to produce specific colors and patterns. From blue and lutino to pied and albino, each mutation offers unique beauty and challenges. By selecting the right pairs and understanding the genetics behind these mutations, you can successfully breed a variety of stunning budgerigars. In the next sections, we’ll delve into setting up the perfect breeding environment and the breeding process itself. Stay tuned for more tips and insights on achieving your dream budgie colors.
Patterns in Budgerigars
Budgerigars, with their vibrant colors and diverse patterns, are a delight to both breeders and bird enthusiasts. Understanding the various patterns in budgerigars is essential for anyone looking to breed these beautiful birds for specific aesthetic traits. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most common and visually striking patterns found in budgerigars.
The Pied Pattern
One of the most popular patterns in budgerigars is the pied pattern. Pied budgerigars have irregular patches of color and white or yellow, creating a striking contrast. This pattern is caused by a dominant gene, meaning only one parent needs to carry the pied gene to produce pied offspring. The distribution of the patches can vary widely, making each pied budgie unique.
The Spangle Pattern
Spangle budgerigars are known for their distinctive feather edges, which are lighter in color than the rest of their plumage. This creates a spangled effect that is both elegant and eye-catching. The spangle pattern is a dominant trait, so it’s relatively easy to produce spangle offspring by breeding a spangle parent with a non-spangle bird.
The Opaline Pattern
The opaline pattern changes the typical distribution of markings on a budgerigar. In opaline budgies, the usual dark markings on the back and wings are replaced by lighter, more vibrant colors, allowing the base color to show through more prominently. The opaline gene is dominant, so only one parent needs to carry the gene to pass it on to their chicks.
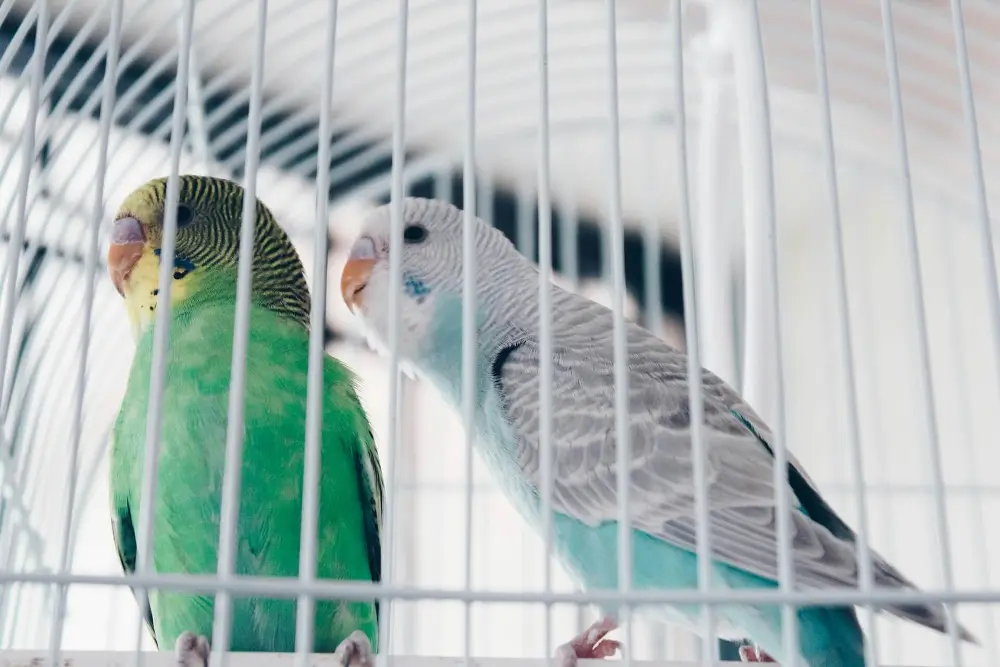

Two spangle opaline budgerigars, one green and one blue, perched inside a breeding cage.
The Clearwing Pattern
Clearwing budgerigars have wings with very light or almost white markings, creating a dramatic contrast with their body color. This pattern is a recessive trait, meaning both parents need to carry the clearwing gene to produce clearwing offspring. The clearwing pattern is particularly striking and adds an elegant touch to any budgie collection.
The Greywing Pattern
Greywing budgerigars have diluted markings, giving them a softer, pastel-like appearance. This recessive mutation reduces the intensity of the bird’s normal color, resulting in a gentle, subdued look. Breeding greywing budgerigars requires both parents to carry the greywing gene.
The Cinnamon Pattern
Cinnamon budgerigars exhibit a warm, brownish hue in their markings instead of the usual black or grey. This sex-linked recessive mutation lightens the bird’s markings, giving them a soft, appealing look. Breeding cinnamon budgerigars involves understanding sex-linked genetics, as this pattern is carried on the sex chromosomes.
The Lacewing Pattern
Lacewing budgerigars have a combination of the clearwing and cinnamon patterns. They have light-colored wings with soft, brownish markings, creating a delicate lace-like appearance. This pattern is recessive, so both parents must carry the lacewing gene to produce lacewing offspring. Lacewings are admired for their graceful and gentle look.
The Recessive Pied Pattern
Recessive pied budgerigars have an even more dramatic pied pattern compared to dominant pied budgies. The recessive pied gene creates a bird with large patches of color and white, often with fewer markings on the face and head. Both parents must carry the recessive pied gene to produce recessive pied offspring.
Patterns in budgerigars add to their charm and make breeding these birds an exciting and rewarding hobby. From the bold pied and spangle patterns to the delicate lacewing and greywing, each pattern offers a unique beauty. By understanding the genetics behind these patterns and selecting the right breeding pairs, you can create a variety of stunning budgerigars with specific colors and patterns. In the next sections, we’ll discuss setting up the perfect breeding environment and the breeding process itself. Stay tuned for more valuable tips and insights on becoming a successful budgerigar breeder.
Setting Up a Breeding Environment
Creating an ideal breeding environment is essential for successfully breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns. A well-prepared environment ensures the health and comfort of your birds, increasing the chances of successful mating and healthy chicks. In this section, we’ll cover the key aspects of setting up a breeding environment that will help you achieve your budgerigar breeding goals.
Choosing the Right Cage
The first step in setting up a breeding environment is selecting the right cage. A spacious breeding cage is crucial to provide enough room for the birds to move around and feel comfortable. Ideally, the cage should be large enough to accommodate nesting boxes and perches without crowding the space. For breeding pairs, a cage size of at least 30 inches long, 18 inches wide, and 18 inches high is recommended.
Nesting Boxes
Nesting boxes are a vital component of the breeding environment. These boxes provide a safe and comfortable place for the female to lay her eggs and raise her chicks. Ensure the nesting box is clean, secure, and placed in a quiet part of the cage to minimize disturbances. Line the nesting box with soft materials like wood shavings or shredded paper to create a cozy nesting area.
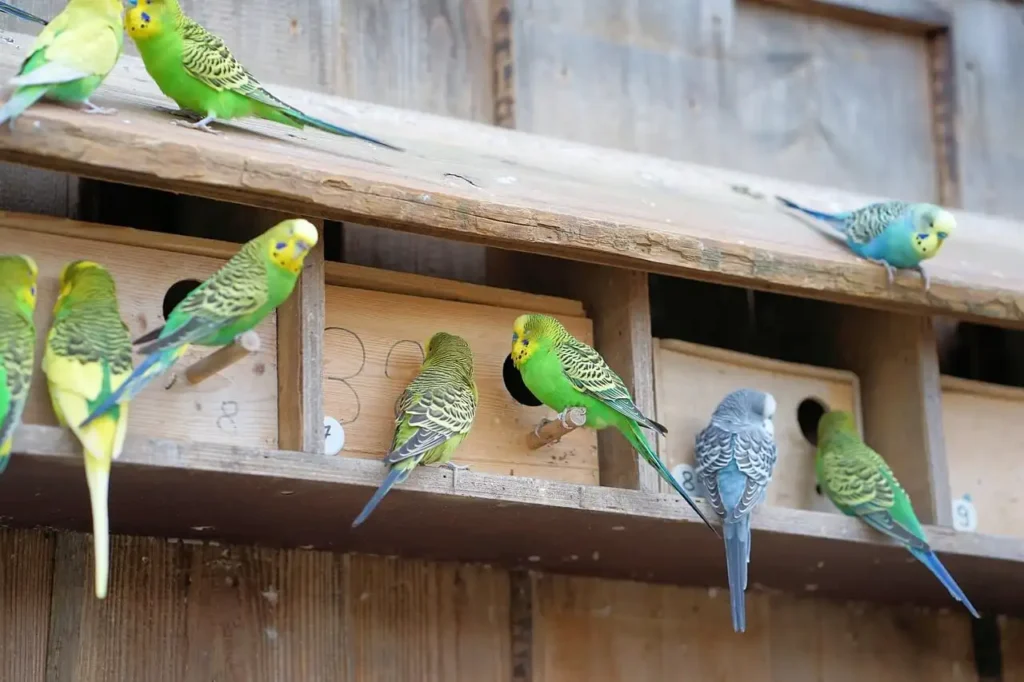

A well-organized breeding cage setup, housing multiple budgerigars with various color mutations.
Perches and Toys
Including a variety of perches in the breeding cage helps keep the birds’ feet healthy and provides different vantage points for them to observe their surroundings. Use perches of varying diameters and materials to mimic their natural habitat. Additionally, provide toys and other enrichment items to keep the birds mentally stimulated and reduce stress.
Diet and Nutrition
A nutritious diet is crucial for the health and fertility of your breeding budgerigars. Provide a balanced diet that includes high-quality seeds, fresh fruits, and vegetables. Supplement their diet with cuttlebone or mineral blocks to ensure they receive essential minerals and vitamins. During the breeding season, consider adding calcium supplements to support egg production.
Lighting and Temperature
Proper lighting and temperature control are important factors in creating an ideal breeding environment. Budgerigars thrive in natural light, so place the cage in a well-lit area but avoid direct sunlight, which can overheat the birds. Maintain a consistent temperature around 70-75°F (21-24°C) to keep the birds comfortable. Using a full-spectrum light can also help simulate natural daylight, promoting healthy breeding behavior.
Hygiene and Cleanliness
Maintaining a clean environment is crucial for the health of your breeding budgerigars. Regularly clean the cage, perches, toys, and nesting boxes to prevent the buildup of bacteria and parasites. Replace the bedding material in the nesting boxes frequently to keep it fresh and hygienic.
Minimizing Stress
Minimizing stress is key to successful breeding. Place the breeding cage in a quiet, low-traffic area where the birds can feel secure. Avoid sudden loud noises or movements that might startle the birds. Provide privacy by covering part of the cage with a cloth or placing it in a secluded spot.
Monitoring and Record Keeping
Keep a close eye on your breeding pairs and monitor their behavior daily. Look for signs of bonding and mating, such as mutual preening and feeding. Keep detailed records of breeding pairs, mating dates, egg laying, and hatching. This information will be invaluable for tracking the success of your breeding program and making informed decisions in the future.
Setting up a breeding environment for budgerigars involves careful planning and attention to detail. By choosing the right cage, providing proper nutrition, maintaining cleanliness, and minimizing stress, you can create a comfortable and conducive space for your birds to breed successfully. In the next sections, we’ll dive into the breeding process and how to care for eggs and chicks. Stay tuned for more expert tips and advice on breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns.
The Breeding Process
The breeding process of budgerigars for specific colors and patterns is both fascinating and rewarding. Understanding each step of this process is essential to ensure the health and success of your birds. In this section, we’ll walk you through the key stages of the breeding process, from courtship to hatching.
Courtship and Pair Bonding
The breeding process begins with courtship and pair bonding. Budgerigars exhibit various behaviors to attract a mate, including singing, preening, and feeding each other. It’s essential to observe these behaviors to confirm that your selected pair is compatible. Providing a stress-free environment and ample space will help encourage bonding and successful mating.
Mating
Once a pair has bonded, they will begin mating. Mating usually involves the male performing a courtship display, which includes head bobbing and singing. If the female is receptive, she will allow the male to mount her. This process can occur multiple times a day, increasing the chances of fertilization.
Nesting and Egg Laying
After successful mating, the female will start preparing the nesting box. She will spend more time inside the box, arranging the bedding material to her liking. Within a week or two, she will begin laying eggs, typically one every other day, until she has laid between four to eight eggs.
Incubation
The female budgerigar will incubate the eggs, keeping them warm and turning them regularly to ensure even development. Incubation lasts about 18-21 days. During this period, it’s crucial to minimize disturbances and ensure the female has access to a nutritious diet, fresh water, and calcium supplements to support her health and the development of the eggs.
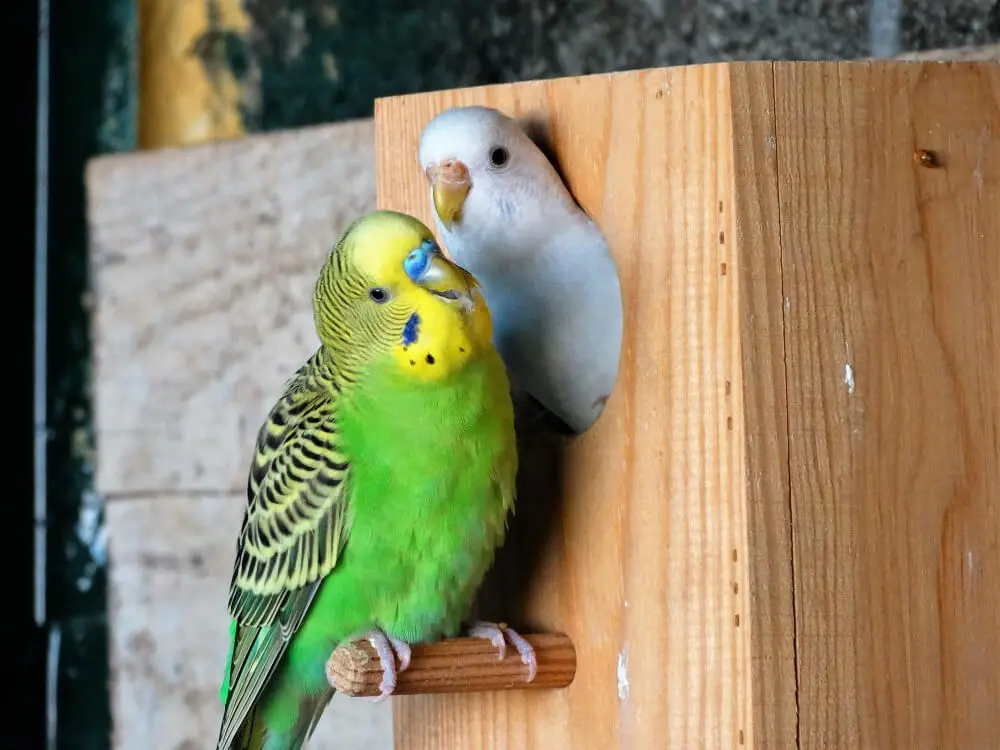

A green budgerigar carefully incubating its eggs inside a cozy nesting box.
Hatching
Once the incubation period is over, the chicks will begin to hatch. This process can take several hours as the chicks break through the eggshell using their egg tooth. It’s important to let nature take its course and avoid interfering unless absolutely necessary. The mother will assist the chicks if they struggle to hatch.
Caring for Chicks
After hatching, the mother budgerigar will care for the chicks, keeping them warm and feeding them regurgitated food. The first few days are critical, as the chicks are very vulnerable. Ensure the breeding environment remains quiet and stress-free to help the mother care for her young effectively.
Monitoring Growth and Development
As the chicks grow, monitor their development closely. They will start to open their eyes and grow feathers within a few weeks. Around four to five weeks old, the chicks will begin exploring outside the nesting box and learning to eat on their own. This period is an excellent time to start handling them gently to socialize them and make them comfortable around humans.
Weaning and Independence
By six to eight weeks, the chicks will be fully feathered and ready to be weaned. Gradually introduce them to a diet of seeds, fruits, and vegetables. Once they are eating independently, they can be separated from their parents and moved to their own cage.
The breeding process of budgerigars for specific colors and patterns is a detailed and rewarding journey. By understanding each stage, from courtship and mating to hatching and weaning, you can ensure the health and success of your breeding program. With patience and careful observation, you’ll be able to achieve your goals of breeding budgerigars with beautiful colors and patterns. In the next sections, we’ll explore how to care for eggs and chicks in more detail and maintain the desired color and pattern in your breeding program. Stay tuned for more expert advice and tips on becoming a successful budgerigar breeder.
Caring for Eggs and Chicks
Caring for eggs and chicks is one of the most critical aspects of breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns. Ensuring that the eggs are properly incubated and the chicks receive the care they need is essential for their healthy development. In this section, we’ll guide you through the best practices for caring for your budgerigar eggs and chicks.
Egg Incubation
Once the female budgerigar has laid her eggs, she will begin the incubation process. It’s important to provide a calm and stable environment to support this critical period.
- Temperature and Humidity: Ensure the nesting box is kept at a consistent temperature around 70-75°F (21-24°C). The humidity should also be maintained at an appropriate level to prevent the eggs from drying out.
- Minimal Disturbance: Avoid handling the eggs unless absolutely necessary. Excessive handling can lead to stress and negatively impact the development of the embryos.
- Check for Fertility: After about a week, you can candle the eggs to check for fertility. Using a small flashlight, gently illuminate the egg to see if veins are developing inside. Fertile eggs will show a network of veins, while infertile ones will appear clear.
Hatching Process
When the incubation period of 18-21 days is over, the chicks will start to hatch. This is a delicate process that requires patience and minimal interference.
- Patience is Key: The hatching process can take several hours. It’s important to let the chicks hatch naturally without intervening unless absolutely necessary.
- Supportive Environment: Ensure the nesting box remains warm and undisturbed during this time. The mother budgerigar will often assist the chicks if they are struggling.
Early Chick Care
Once the chicks have hatched, the mother will take on the primary role of caring for them, but your support is still crucial.
- Feeding: The mother will feed the chicks regurgitated food. Ensure she has access to a nutritious diet rich in protein, calcium, and vitamins to support her and her chicks.
- Warmth: Newly hatched chicks are extremely vulnerable and need warmth. The mother will keep them warm, but ensure the surrounding environment remains at a stable, comfortable temperature.
- Cleanliness: Maintain a clean nesting box to prevent the buildup of bacteria and parasites. Replace the bedding material as needed to keep it fresh and hygienic.
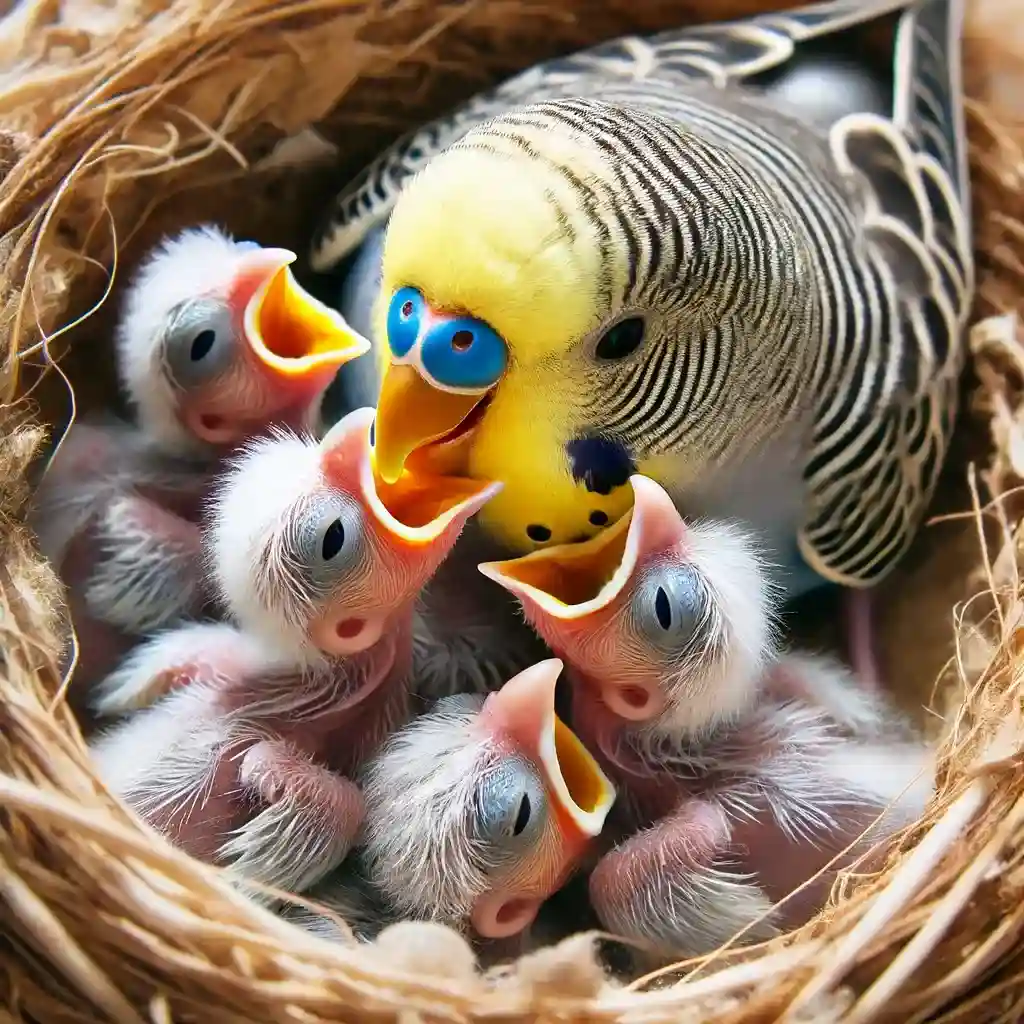

An adult budgerigar attentively feeding its hungry chicks nestled in a cozy nest.
Monitoring Growth and Development
As the chicks grow, it’s important to monitor their development closely to ensure they are progressing healthily.
- Weight and Size: Keep track of the chicks’ weight and size. Healthy chicks will gain weight steadily and start to show feather development within a few weeks.
- Feathering: Around two to three weeks old, chicks will begin to develop their feathers. This is a good time to start handling them gently to get them used to human interaction.
- Weaning: By six to eight weeks, chicks should be fully feathered and starting to eat on their own. Gradually introduce them to a diet of seeds, fruits, and vegetables.
Weaning and Independence
When the chicks are ready to be weaned, it’s time to help them transition to independence.
- Introduce Solid Foods: Gradually introduce a variety of foods to encourage the chicks to start eating independently. Provide a mix of seeds, fresh fruits, and vegetables.
- Separate from Parents: Once the chicks are eating on their own, they can be moved to a separate cage. This helps prevent any potential aggression from the parents as the chicks grow more independent.
Caring for eggs and chicks is a rewarding and delicate part of breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns. By providing a stable environment, ensuring proper nutrition, and monitoring their development, you can help ensure the health and success of your budgerigar chicks. In the following sections, we’ll discuss how to maintain color and pattern consistency in your breeding program and address any health considerations. Stay tuned for more expert advice on becoming a successful budgerigar breeder.
Monitoring and Maintaining Color and Pattern
Monitoring and maintaining the color and pattern of budgerigars is a critical aspect of breeding these beautiful birds. Achieving and preserving specific color mutations and patterns requires careful observation, record-keeping, and selective breeding practices. In this section, we’ll explore how to effectively monitor and maintain the desired color and pattern in your budgerigars.
Consistent Record-Keeping
To maintain specific colors and patterns in your breeding program, meticulous record-keeping is essential. Keeping detailed records of each bird’s genetic background, color mutations, and breeding outcomes will help you make informed decisions in future pairings.
- Pedigree Charts: Create pedigree charts to track the lineage of your birds. This helps you understand which genes are present in your breeding stock and how they might combine in future generations.
- Breeding Logs: Maintain breeding logs that document the pairs you’ve bred, the dates of mating, egg laying, hatching, and the color and pattern of the offspring. This data is invaluable for planning future pairings and predicting outcomes.
Selective Breeding
Selective breeding is the cornerstone of maintaining and enhancing specific colors and patterns in budgerigars. By carefully choosing pairs that carry the desired genes, you can increase the likelihood of producing chicks with those traits.
- Genetic Compatibility: Ensure that the pairs you select have compatible genetic backgrounds. For example, to breed blue budgerigars, both parents should carry the recessive blue gene.
- Desired Traits: Focus on pairs that exhibit the desired color and pattern traits. If you aim to breed spangle budgerigars, at least one parent should have the spangle pattern.
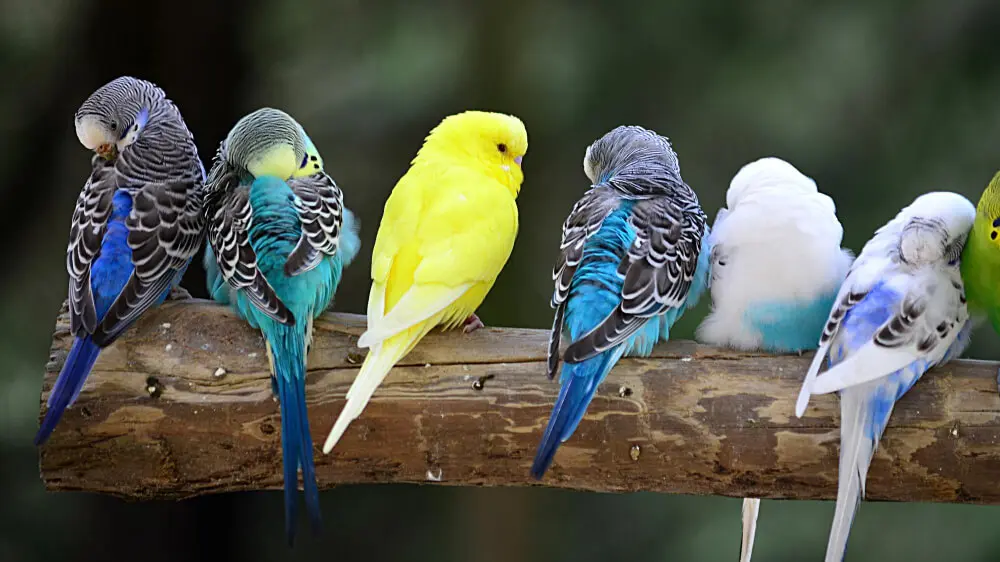

A diverse group of budgerigars showcasing a range of colors and patterns, thriving in an aviary.
Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of your budgerigars is crucial to ensure their health and the integrity of their colors and patterns.
- Health Checks: Conduct regular health checks to ensure your birds are in optimal condition. Healthy birds are more likely to produce vibrant, well-patterned offspring.
- Feather Quality: Monitor the quality of your birds’ feathers. Poor feather quality can indicate health issues or nutritional deficiencies that need to be addressed.
Nutritional Support
Proper nutrition plays a significant role in maintaining the color and pattern of your budgerigars. A balanced diet helps ensure that your birds display their full genetic potential.
- Balanced Diet: Provide a balanced diet that includes high-quality seeds, fresh fruits, and vegetables. This ensures your birds receive all the necessary nutrients for vibrant plumage.
- Supplements: Consider adding supplements like vitamins and minerals to support overall health and feather quality, especially during the breeding season.
Avoiding Inbreeding
Inbreeding can lead to genetic problems and a decrease in the quality of colors and patterns. It’s important to avoid breeding closely related birds to maintain a healthy and diverse gene pool.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new birds into your breeding program periodically to maintain genetic diversity. This helps prevent inbreeding and promotes the overall health of your flock.
- Careful Pair Selection: Always check the genetic background of potential pairs to ensure they are not closely related.
Addressing Color Fading
Sometimes, budgerigar colors can fade due to various factors such as age, diet, or health issues. If you notice color fading, take steps to address the underlying causes.
- Dietary Adjustments: Ensure your birds are receiving a nutrient-rich diet. Lack of certain nutrients can lead to dull or faded colors.
- Health Interventions: Consult with an avian veterinarian if you suspect health issues are causing color fading. Treating underlying health problems can help restore vibrant plumage.
Monitoring and maintaining the color and pattern of budgerigars is a continuous process that requires careful attention to genetics, health, and nutrition. By keeping detailed records, practicing selective breeding, and providing optimal care, you can achieve and preserve the beautiful colors and patterns that make budgerigars so special. In the next sections, we’ll delve into health considerations for breeding budgerigars and ethical breeding practices. Stay tuned for more insights and tips on successful budgerigar breeding.
Health Considerations in Breeding
When breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns, prioritizing the health of your birds is essential. Healthy budgerigars are more likely to produce strong, vibrant offspring, and maintaining their well-being is crucial for a successful breeding program. In this section, we’ll discuss the key health considerations you need to keep in mind when breeding budgerigars.
Pre-Breeding Health Check
Before starting the breeding process, it’s vital to ensure that both potential parents are in excellent health. A pre-breeding health check can help identify and address any issues that might affect breeding success.
- Veterinary Examination: Schedule a thorough check-up with an avian veterinarian. This will help detect any underlying health problems and ensure your birds are fit for breeding.
- Nutritional Assessment: Assess the birds’ diet to ensure they are receiving adequate nutrition. A balanced diet is crucial for their overall health and reproductive success.
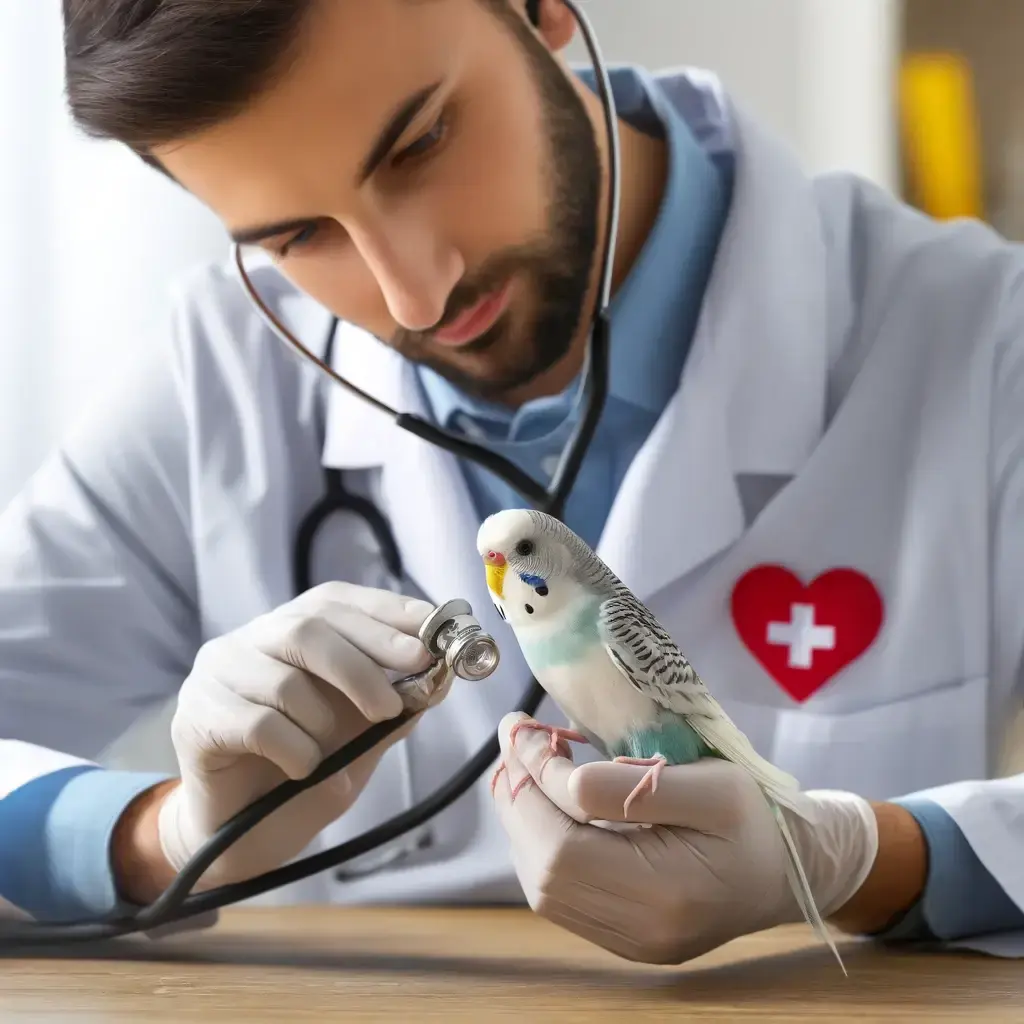

An avian veterinarian conducting a health check-up on a budgerigar, ensuring its well-being for breeding purposes.
Optimal Diet and Nutrition
Providing a nutritious diet is one of the most important aspects of keeping your breeding budgerigars healthy.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure your birds have a balanced diet that includes high-quality seeds, fresh fruits, and vegetables. A variety of foods will provide essential vitamins and minerals.
- Calcium Supplements: During the breeding season, calcium supplements are essential to support egg production and prevent deficiencies. Cuttlebone or mineral blocks are great sources of calcium.
- Protein-Rich Foods: Include protein-rich foods such as boiled eggs, legumes, and sprouted seeds to support the increased nutritional needs of breeding birds.
Disease Prevention
Preventing diseases is crucial to maintaining a healthy breeding flock. Implementing good hygiene practices and monitoring for signs of illness can help keep your birds disease-free.
- Clean Environment: Regularly clean the breeding cages, perches, and nesting boxes to prevent the buildup of bacteria and parasites.
- Quarantine New Birds: Quarantine any new birds for at least 30 days before introducing them to your breeding flock. This helps prevent the spread of diseases.
- Monitor for Symptoms: Keep an eye out for signs of illness, such as changes in behavior, feather quality, or droppings. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing the spread of disease.
Stress Management
Minimizing stress is crucial for the health and well-being of your breeding budgerigars. Stress can negatively impact their reproductive success and overall health.
- Quiet Environment: Place breeding cages in a quiet, low-traffic area to minimize disturbances. Avoid sudden loud noises and movements that might startle the birds.
- Adequate Space: Ensure the breeding cage is spacious enough to allow for natural behaviors and reduce stress. Overcrowded conditions can lead to aggression and stress-related health issues.
Genetic Health
Maintaining genetic diversity is important to prevent inherited health problems and ensure the long-term health of your breeding stock.
- Avoid Inbreeding: Avoid breeding closely related birds to prevent genetic disorders and health issues associated with inbreeding.
- Introduce New Genetics: Periodically introduce new birds into your breeding program to maintain genetic diversity and strengthen your flock’s overall health.
Post-Breeding Care
After the breeding season, it’s essential to continue caring for the health of your breeding pairs and their offspring.
- Recovery Period: Allow breeding pairs a recovery period to rest and regain their strength. Provide a nutritious diet and a stress-free environment.
- Chick Health Monitoring: Monitor the health of the chicks as they grow. Ensure they receive proper nutrition and check for any signs of health issues.
Prioritizing health considerations in breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns is crucial for a successful breeding program. By ensuring your birds receive proper nutrition, maintaining a clean and stress-free environment, and preventing diseases, you can help your budgerigars thrive and produce healthy, vibrant offspring. In the next sections, we’ll explore ethical breeding practices and answer some frequently asked questions about breeding budgerigars. Stay tuned for more expert advice on becoming a successful budgerigar breeder.
Ethical Breeding Practices
Breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns can be a rewarding endeavor, but it is essential to adhere to ethical breeding practices. Ensuring the welfare of your birds should always be your top priority. In this section, we’ll discuss ethical breeding practices that every responsible breeder should follow.
Prioritizing Bird Welfare
The welfare of your budgerigars must come first in any breeding program. Ethical breeders focus on the health, comfort, and well-being of their birds above all else.
- Health and Nutrition: Provide a balanced diet, regular health checks, and a clean environment to keep your birds healthy and happy.
- Avoid Overbreeding: Do not breed birds excessively. Give them ample time to rest and recover between breeding cycles to prevent physical and emotional stress.
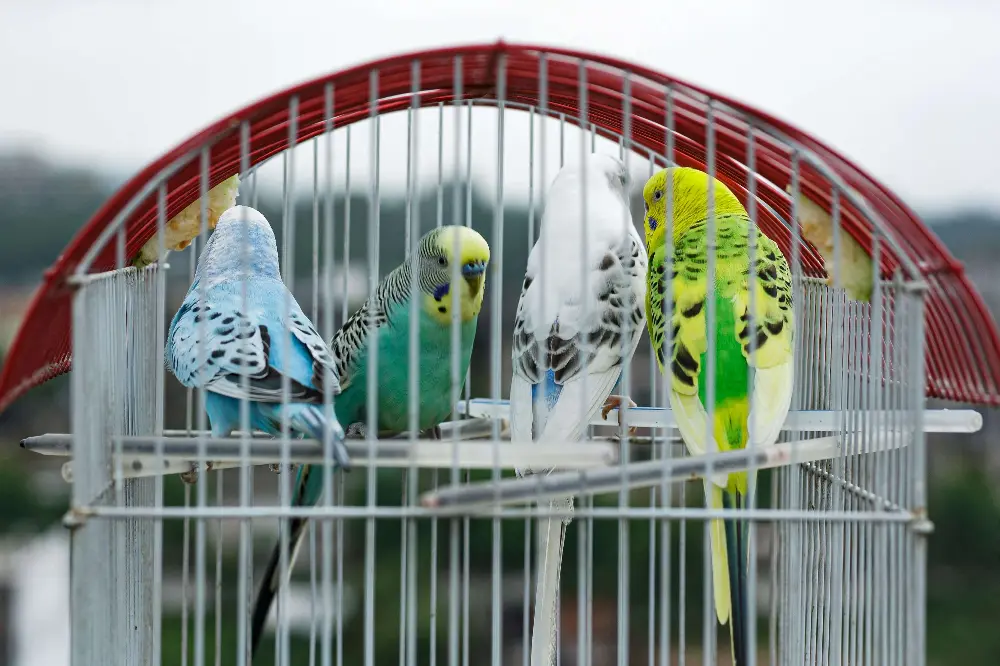

A group of healthy budgerigars displaying a range of colors, housed in a spacious cage.
Responsible Pair Selection
Choosing the right pairs for breeding involves more than just color and pattern; it includes considering the birds’ health, genetics, and compatibility.
- Genetic Diversity: Avoid inbreeding by selecting pairs that are not closely related. This helps maintain a healthy gene pool and prevents genetic disorders.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the pairs you select get along well and do not exhibit aggressive behavior toward each other.
Ethical Breeding Environment
Creating a safe and nurturing environment is crucial for ethical breeding.
- Adequate Space: Provide spacious breeding cages that allow birds to move freely and engage in natural behaviors.
- Nesting Boxes: Ensure nesting boxes are clean, secure, and placed in a quiet area to reduce stress.
Transparency and Honesty
Ethical breeders are transparent about their breeding practices and the health of their birds.
- Accurate Records: Keep detailed records of your breeding program, including health checks, genetic backgrounds, and breeding outcomes. Share this information with potential buyers.
- Honesty with Buyers: Be honest with potential buyers about the birds’ health, genetic history, and any known issues. This builds trust and ensures the birds go to informed and caring homes.
Avoiding Exploitation
Breeding should never be done solely for profit or at the expense of the birds’ well-being.
- Fair Pricing: Price your birds fairly, considering the care and resources required to breed and raise them ethically.
- Avoid Mass Breeding: Focus on quality over quantity. Mass breeding often leads to neglect and poor living conditions for the birds.
Education and Advocacy
Ethical breeders educate themselves and others about responsible breeding practices and advocate for bird welfare.
- Continuous Learning: Stay informed about the latest best practices in bird breeding and care. Attend workshops, join breeder associations, and consult with avian veterinarians.
- Educate Buyers: Provide new bird owners with information on proper care, nutrition, and breeding ethics. This helps ensure the birds continue to receive excellent care in their new homes.
Commitment to Animal Welfare
Above all, ethical breeders are committed to the welfare of their animals.
- Rescue and Adoption: Consider adopting or rescuing budgerigars in need of homes, and encourage others to do the same.
- Supporting Welfare Organizations: Support and collaborate with animal welfare organizations to promote responsible breeding and bird care.
Ethical breeding practices are essential for the well-being of your budgerigars and the success of your breeding program. By prioritizing bird welfare, practicing responsible pair selection, maintaining a healthy environment, and being transparent with buyers, you can breed budgerigars for specific colors and patterns ethically and responsibly. In the next section, we’ll answer some frequently asked questions about breeding budgerigars. Stay tuned for more insights and tips on becoming a successful and ethical budgerigar breeder.
FAQs about Breeding Budgerigars for Specific Colors and Patterns
Breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns can be an intriguing and rewarding process. To help you navigate this fascinating hobby, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions. These answers will provide valuable insights and practical advice for both novice and experienced breeders.

A playful illustration of colorful budgerigars with question marks, representing common questions about budgerigar breeding.
What are the most common color mutations in budgerigars?
Common color mutations in budgerigars include blue, lutino, pied, albino, cinnamon, opaline, spangle, and greywing. Each mutation offers unique and beautiful variations in color and pattern, making budgerigars one of the most visually diverse pet birds.
How can I predict the color and pattern of the offspring?
Predicting the color and pattern of budgerigar offspring involves understanding the genetics of the parent birds. Knowing whether a color trait is dominant or recessive helps in predicting outcomes. For example, breeding blue budgerigars requires both parents to carry the recessive blue gene.
What is the best age for budgerigars to start breeding?
Budgerigars should be at least one year old before they start breeding. This ensures they are physically mature and ready to handle the demands of breeding and raising chicks. Breeding too early can lead to health complications for both the parents and their offspring.
How do I select the right breeding pairs?
Selecting the right breeding pairs involves considering genetic compatibility, health, and the specific color and pattern traits you aim to achieve. Ensure both birds are healthy, compatible, and carry the desired genes for the colors and patterns you want to produce.
What should I feed my breeding budgerigars?
A balanced diet is crucial for breeding budgerigars. Provide high-quality seeds, fresh fruits, and vegetables, and include calcium supplements to support egg production. Protein-rich foods like boiled eggs and legumes are also beneficial during the breeding season.
How do I ensure the health of my breeding budgerigars?
Regular health checks, a clean environment, and a nutritious diet are key to ensuring the health of your breeding budgerigars. Monitor for signs of illness and consult an avian veterinarian if you notice any health issues.
How long does the incubation period last?
The incubation period for budgerigar eggs is typically 18-21 days. During this time, the female budgerigar will incubate the eggs, keeping them warm and turning them regularly to ensure even development.
How can I minimize stress for my breeding budgerigars?
Minimize stress by placing the breeding cage in a quiet, low-traffic area. Provide ample space, avoid sudden loud noises, and ensure the environment is stable and comfortable. Stress can negatively impact breeding success and the health of your birds.
What are some common challenges in breeding budgerigars?
Common challenges in breeding budgerigars include health issues, genetic problems due to inbreeding, and environmental stress. Ensuring proper care, genetic diversity, and a stress-free environment can help mitigate these challenges.
How can I avoid inbreeding?
Avoid inbreeding by selecting breeding pairs that are not closely related and introducing new birds into your breeding program periodically. This maintains genetic diversity and prevents health issues associated with inbreeding.
What should I do if a chick is not developing properly?
If a chick is not developing properly, consult an avian veterinarian for advice. Ensure the chick is receiving adequate nutrition and warmth, and monitor for any signs of illness or developmental issues.
How can I find homes for the chicks?
Finding homes for budgerigar chicks involves networking with other bird enthusiasts, posting in local pet groups, and working with reputable pet stores or bird clubs. Ensure potential buyers are knowledgeable about budgerigar care and committed to providing a good home.
Breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns involves understanding genetics, selecting the right pairs, and maintaining a healthy, stress-free environment. By addressing these frequently asked questions, we hope to provide you with the knowledge and confidence to embark on your breeding journey. Stay tuned for more expert tips and insights on successful budgerigar breeding.
Conclusion
Breeding budgerigars for specific colors and patterns is a rewarding and fascinating endeavor that requires knowledge, patience, and dedication. By understanding the genetics behind budgerigar color mutations, selecting the right breeding pairs, and maintaining a healthy and stress-free environment, you can achieve stunning results.
Throughout this guide, we’ve covered essential topics such as setting up a breeding environment, caring for eggs and chicks, monitoring and maintaining color and pattern, and adhering to ethical breeding practices. Each step in the breeding process is crucial for the health and well-being of your birds, and ultimately, for the success of your breeding program.
By following ethical breeding practices, prioritizing the welfare of your budgerigars, and staying informed about best practices, you can become a successful budgerigar breeder. Remember, the goal is not only to produce beautiful birds but also to ensure their health and happiness.

A pair of budgerigars, one with blue plumage and the other with a mix of yellow and green, sharing a moment on a branch.
As you start your breeding journey, keep detailed records, provide optimal nutrition, and continuously educate yourself about budgerigar care and genetics. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced breeder, the joy of seeing vibrant, healthy chicks emerge and grow into beautiful adults is immensely gratifying.
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights and practical advice to help you breed budgerigars with specific colors and patterns successfully. Stay committed to ethical breeding practices, and enjoy the incredible experience of nurturing and raising these wonderful birds.

